Differentiate between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Long bones may suffer from different types of fractures.

Interstitial And Appositional Growth Bartleby
The different cell types present in bone are illustrated in Fig.

. Types of Bone Cells. The process of the formation of bones is known as ossification or osteogenesis. New bone matrix is added to the outside of the bone surface while the medullary cavity is increased broadening the diameter of the bone overall.
Actively participates in bone growth and repair Perforating fibers allow for strong attachment. Name the cells that produce cartilage. Osteoclasts resorb old bone that lines the medullary cavity while osteoblasts via intramembranous ossification produce new bone tissue beneath the periosteum.
Route for blood and nervous supply 3. Osteoblasts bone lining cells and osteoclasts are present on bone surfaces and are derived from local mesenchymal cells called progenitor cells. Osteoblast synthesizes the bone matrix and are responsible for its mineralization.
This growth can be commonly observed after birth of an individual but generally in the first trimester that is. Osteoblasts osteocytes osteoclasts and bone lining cells. Endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification.
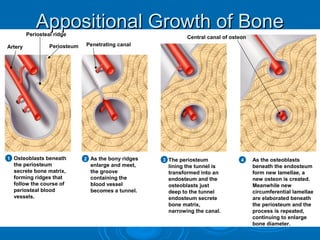
Bone Formation and Remodelling. Appositional growth growth of a bone by addition of bone tissue to its surface Bone is resorbed at endosteal surface and added at periosteal surface Osteoblasts add bone tissue to the external surface of the diaphysis Osteoclasts remove bone from the. Interstitial growth produces longer bones as the cartilage lengthens and is replaced by bone tissue while appositional growth occurs when new bone tissue is deposited on the surface of the bone resulting in bone thickening.
Osteocytes permeate the interior of the bone and are produced from the fusion of mononuclear blood. Bone formation in the human body begins during fetal development. A normal bone ossification process can be of two different types.
This increase in the length size of the bone is referred as interstitial growth whereas the increase in the preexisting diameter or width size of bones is referred as appositional growth. Appositional bone growth The periosteum Wraps the superficial layer of compact bone Two layers 1. Endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification are the two methods of bone formation.
Osteoblasts secrete additional collagen which is then calcified creating strands of trabecula. What is Endochondral Ossification Definition Types of Bones Steps 2. Osteoblasts are the cells involved in the bone formation.
Bone is composed of four different cell types. Layers of bone tissues are laid by osteoblasts. Be able to recognize these cell types.
Both the compact and spongy bone tissues are composed of 3 main types of bone cells. Isolates bone from surrounding tissues 2. Fibrous outer layer 2.
Contains red bone marrow which produces blood cells. A cell that releases calcium from bone increasing blood calcium levels. Parathyroid hormone PTH activates this type of cell.
After birth endochondral ossification performs a major role in bone elongation which is accomplished through the epiphyseal plate. A mature bone cell trapped in bone matrix. They each unique functions and are derived from two different cell lines Figure 1 and Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7.
Ossification at the epiphyseal plate involves removing the hyaline cartilage model before laying down new bone matrix which results in a longer. These bone cells are Osteoclasts Osteoblasts and Osteocytes. Bone ossification is not the same as bone calcification process.
Osteoblasts osteocytes and osteoclasts. Contains yellow bone marrow which stores triglycerides fats. These bone cells are embedded in the matrix of bony tissue and perform many vital functions.
Growth in bones occurs in two ways either longitudinally or increase in the width of bone size. Cellular inner layer Functions 1. It is a process which involves the laying of calcium-based salts within the cells and tissues.
Classify bones by shape and give examples. Describe interstitial and appositional growth. The erosion of old bone along the medullary cavity and the deposition of new bone beneath the periosteum not only increase the diameter of the diaphysis but also increase the.
The appositional growth of bones is a. The remodeling cycle consists of three consecutive phases. This is called appositional growth.
Bone remodeling involves the removal of mineralized bone by osteoclasts followed by the formation of bone matrix through the osteoblasts that subsequently become mineralized. The skeleton is a metabolically active organ that undergoes continuous remodeling throughout life. The cell responsible for the resorption of bone matrix is the osteoclast a large motile multinucleated cell located on bone surfaces tightly associated with the calcified matrix.
Osteoblasts osteocytes osteogenic cells and osteoclasts. These bone cells have distinct features structure and considered essential functions. The outer layer of pluripotent cells which support appositional growth over areas replaced with bone is now called the periosteum.
Appositional growth is bine growth in width by adding new layers interstitial growth is bone growh in length from within. What is appositional bone growth. Name the different types of cartilage and the location in the human body.
Be able to describe as well as recognize in microscope sectionsphotos the process of intramembranous bone formation including the process by which cancellous bone is converted into compact bone. Name five anatomical structures of a long bone. Four types of cells are found within bone tissue.
A cell that stores calcium in bone by making bone matrix. Doctors describe fractures to other doctors using classification systems. After birth a persons bones grow in length and thickness.
Appositional growth occurs during bone remodeling.

6 4 Bone Formation And Development Anatomy Physiology

Difference Between Interstitial And Appositional Growth Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
0 Comments